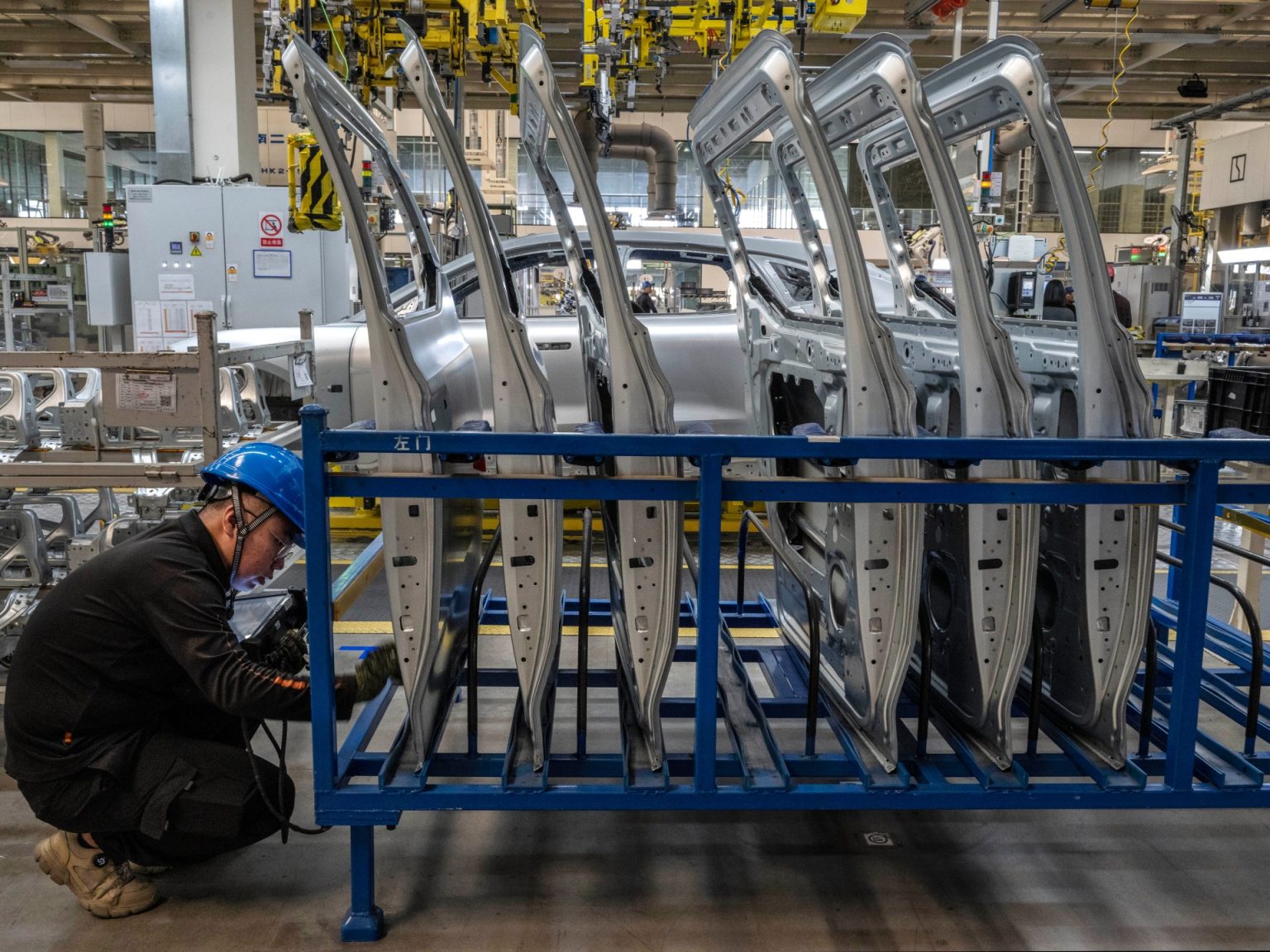
The Chinese economy continues to grapple with lingering challenges, as recent data reveals a persistent slowdown in manufacturing activity. November marks the eighth consecutive month of contraction in the sector, a stretch not seen since data collection began, according to Bloomberg. This ongoing situation impacts global markets and raises questions about the strength of the world’s second-largest economy. Understanding the current state of النشاط الصناعي في الصين (China’s industrial activity) is crucial for businesses and investors alike.
استمرار انكماش النشاط الصناعي في الصين (Continued Contraction of China’s Industrial Activity)
Bloomberg’s latest report highlights a worrying trend: China’s manufacturing sector remains firmly in contraction territory. The official Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) for manufacturing registered 49.2 in November, falling short of the expected 49.4 and remaining below the 50-point threshold that signifies growth. This isn’t an isolated incident; the extended period of decline underscores deep-seated weaknesses within the Chinese economic landscape.
The data, while showing slight improvement over previous months, isn’t sufficient to signal a robust recovery. The prolonged weakness signals a need for careful analysis of the factors contributing to this slowdown. This persistent contraction is a key indicator of broader economic challenges.
تراجع قطاعي التصنيع والخدمات (Decline in Manufacturing and Service Sectors)
The downturn isn’t limited to manufacturing. Bloomberg reports that the services sector has also begun to falter. The official non-manufacturing PMI – encompassing services and construction – declined to 49.5 in November, a significant drop from October’s 50.1. This represents the first contraction in nearly three years, driven primarily by weakness in the property market and related services.
تأثير ضعف العقارات (Impact of the Weak Property Market)
The real estate sector, once a major driver of Chinese economic growth, continues to be a significant drag. Falling property values, coupled with reduced construction activity, are impacting demand for related services, contributing to the overall decline in the non-manufacturing PMI. This situation is particularly concerning as the housing market plays a vital role in Chinese household wealth and investment.
التوترات التجارية وتأثيرها على الاقتصاد (Trade Tensions and Their Impact on the Economy)
Global trade dynamics are adding further pressure on the Chinese economy. While a temporary ‘truce’ in the trade war with the United States, following a meeting between Presidents Trump and Xi, offered a brief respite, the details remain unresolved. Specifically, discussions regarding China’s exports of rare earth minerals to the US are ongoing, highlighting the fragility of the current understanding.
Meanwhile, a recent diplomatic dispute with Japan has further intensified trade uncertainties. Beijing is reportedly considering counter-economic measures. These geopolitical factors contribute to the overall climate of economic instability. International trade is a key component of China’s growth, and disruptions can have significant consequences.
ضعف الطلب المحلي (Weak Domestic Demand)
A major issue confronting the Chinese economy is declining domestic demand. October saw a fifth consecutive month of falling retail sales, the longest such streak since the major lockdowns during the pandemic. This indicates that consumers are being hesitant to spend.
Additionally, the weak الاستهلاك في الصين (consumption in China) is causing concern. This slowdown is particularly worrying as the government had hoped that robust domestic consumption would help offset weakening export demand. It’s a critical sign that even with easing COVID-19 restrictions, consumer confidence hasn’t fully recovered.
استجابة الحكومة للتباطؤ الاقتصادي (Government Response to the Economic Slowdown)
Despite the economic headwinds, Chinese policymakers haven’t rushed into implementing large-scale stimulus packages. They appear confident in achieving their annual growth target of around 5%. Since September, the government has already introduced a series of measures amounting to one trillion yuan (approximately $141 billion).
These measures include the release of unused bond quotas for local governments, settling outstanding payments to businesses, and providing new funding to policy banks to support investment. While these initiatives are significant, the government’s measured approach suggests a preference for targeted support rather than an all-out stimulus. Focus is also being directed toward boosting التكنولوجيا والتصنيع (technology and manufacturing) as long-term growth pillars.
التركيز المستقبلي على التكنولوجيا والتصنيع (Future Focus on Technology and Manufacturing)
Beijing has clearly signaled its intention to prioritize technological advancement and manufacturing capabilities in the coming years. Despite commitments to increase the contribution of consumption to the economy, it’s evident that industrial policy remains central to China’s development strategy. This focus on high-value sectors is designed to enhance China’s global competitiveness and reduce its reliance on external markets.
However, analysts predict a further slowdown in export growth in the current quarter, with figures showing the weakest performance since late 2022. Net exports have contributed considerably to China’s growth this year, but this contribution is expected to diminish. Ultimately, the future trajectory of النشاط الصناعي في الصين hinges on a delicate balance between addressing domestic consumption challenges, navigating geopolitical risks, and successfully implementing its long-term industrial policies.
In conclusion, the situation concerning China’s industrial activity remains complex and warrants close attention. The prolonged contraction, coupled with challenges in the property market, weak domestic demand, and global trade tensions demands careful monitoring. While the government has implemented measures to support the economy, the coming months will be crucial in determining whether these actions are sufficient to trigger a sustainable recovery and steer China toward its ambitious growth goals. Staying informed about these developments is vital for understanding the global economic landscape.